Ford Lotus Cortina Mark I
 |
|
| Production | 1963 to 1966 |
|---|---|
| Class | Sports Car |
| Body style | 2-door saloon |
| Engine | 1,558 cu cm |
| Wheelbase | 98 in (2,489 mm) |
| Length | 168.25 in (4,274 mm) |
| Height | 53.40 in, 1,356 mm |
| Dry weight | 1,863 1b, 845 kg |
The most famous version of Cortina was the Cortina Lotus from the 1960s. Ford had commissioned Colin Chapman.
History
Models of the Lotus Cortina were available as two-door saloons with a contrasting green side flash along each side with front quarter bumpers . Lotus Cortinas had a one-of-a-kind 1557 cc twin-cam Lotus engine based on the Kent OHV engine. Some body panels for the doors, bonnet, and boot were made of aluminium. It also had a unique A-frame rear suspension for a short period, but this proved to be weak, and the vehicle was quickly returned to the conventional Cortina semi-elliptic rear end. Inside a A wood-rimmed steering wheel gauge upgrades to tachometer, speedometer, oil pressure, water temperature. was fitted.
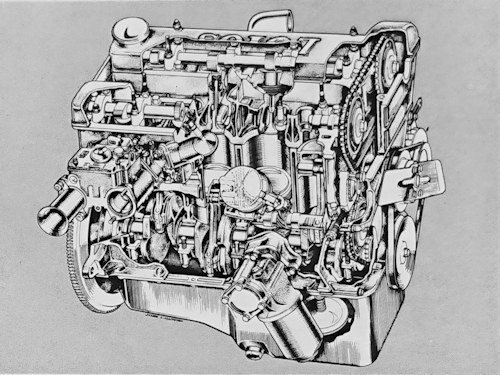
Ford had commissioned Colin Chapman , owner of Lotus Cars , to build a Cortina for motorsport. The Cortina Lotus engine had a Harry Mundy designed alloy cylinder head with dual overhead camshafts on the block of the normal Kent engine. This engine was also used in the Lotus 23 , Lotus Seven and the Lotus Elan . With 2 Weber DCOE 18 horizontal carburettors.
PERFORMANCE
ENGINE CAPACITY 95.07 cu in, 1,558 cu cm
FUEL CONSUMPTION 20.2 ml imp gal, 16.8 ml US gal,
MAX SPEED 108 mph, 173.9 km/h
weight ratio: 17.6 lb/hp, 8 kg/hp
acceleration: 0— 80 km/h) 4.2 sec
standing 1/4 mile 17 sec
The outer skin of the doors and hood of the Cortina Lotus is made of aluminum instead of steel. The chassis of the Lotus Cortina has also been modified. While the rear axle of the series models was attached to leaf springs, the Lotus Cortina had a better guided rear axle with trailing arms, a bottom reaction triangle articulated on the differential housing and coil springs. In addition, the differential housing was made of aluminum to reduce the unsprung mass of the rigid rear axle. The axle tubes were still made of steel. This design proved to be the Lotus Cortina's weak point, as the aluminum housing of the differential was not sufficiently rigid and this led to numerous differential defects, especially in sports use. For this reason, during the "active" period of this sports model, most specimens were converted back to the rear axle of the normal models, which caused fewer problems.Front suspension with telescopic damper struts, lower wishbones, anti-roll bar at the rear rigid Axle, trailing radius arms, wide-based lower A-bracket, coil springs, telescopic dampers fitted.
There were two main variations of the Mark 1. The Mark 1a possessed elliptical front side-lights, whereas the Mark 1b had a re-designed front grille incorporating the more rectangular side-light and indicator units.
The competition model.
Featured upgrades such as engine capacity 97.27 cu in, 1,594 cu cm, bore 3.29 in, 83.5 mm, max power (DIN) 140 hp at 6,500 rpm, max torque (DIN) 125 1b ft,17.3 kg m at 5,000 rpm, 87.8 hp/l specific power, 2 Weber 40 DCOE 2 horizontal twin barrel carburettors, 4.444 axle ratio, on request 4.125 3.900 3.770 axle ratios,5.50 x 13tyres, oil cooler, electric fuel pump, light alloy wheels, competition suspension semi-axles and propeller shaft, enlarged fuel tank. 4.100 axle ratio.
Technical
-
Lotus Cortina MK1 Technical details and specifications
ENGINE
front, 4 stroke
cylinders: 4, vertical, in line
bore and stroke: 3.25 x 2.86 in, 82.5 x 72.7 mm
engine capacity: 95.07 cu in, 1,558 cu cm
compression ratio: 9.5
max power (DIN): 106 hp at 5,500 rpm
max torque (DIN): 104 1b ft, 14.4 kg m at 4,000 rpm
max number of engine rpm: 6,500
specific power: 68 hp/l; cylinder block: cast iron
cylinder head: light alloy, hemispherical combustion chambers
crankshaft bearings: 5
valves: 2 per cylinder, overhead, Vee-slanted, thimble tappets
camshafts: 2, overhead
lubrication: gear pump, full flow filter
carburation: 2 Weber DCOE 18 horizontal carburettors
fuel feed: mechanical pump
cooling system: water
TRANSMISSIONdriving wheels: rear
clutch: single dry plate, hydraulically controlled
gearbox: mechanical
gears: 4 + reverse
synchromesh gears: 1st, 2nd,3rd,4th
gearbox ratios: 1st 2.500, 2nd 1.640, 3rd 1.230, 4th 1, rev 2.810
final drive: hypoid bevel
axle ratio: 3.900.CHASSIS
telescopic damper struts, lower wishbones, anti-roll bar
rear suspension: rigid Axle, trailing radius arms, wide-based lower A-bracket, coil springs, telescopic dampers.STEERING
recirculating ball
turns of steering wheel lock to lock: 3.30.BRAKES
front disc (diameter 9.75 in, 248 mm), rear drum, servo; area linings: total 281.71 sq in, 1,817 sq cm.
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
voltage: 12 V
battery: 38 Ah
dynamo 264 W
ignition distributor: LucasDIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT
wheel base: 98.40 in, 2,499 mm
front track: 51.60 in, 1,311 mm
rear track: 50.39 in, 1,280 mm
overall length: 168.30 in, 4,275 mm
overall width 62.50 in, 1,587 mm
overall height: 53.40 in, 1,356 mm
ground clearance: 5.30 in, 135 mm
dry weight: 1,863 1b, 845 kg
distribution of weight: 54% front axle, 46% rear axle
turning circle (between walls): 32.5 ft, 9.9 m
width of rims: tyres: 6.00 x 13
© Motor car History
Service
-
Lotus Cortina MK1 Service Guide
engine sump oil: SAE 20W-40, change every 1,900 miles, 3,000 km
lubricating system capacity: 7 imp pt, 8.46 US pt
gearbox oil: SAE 80, change every 5,000 miles, 8,000 km
cooling system capacity: 12.75 imp pt, 15.22 US pt, 7.2 1.
final drive oil: SAE 90
steering box oil: SAE 90
greasing: every 5,000 miles, 8,000 km, 8 points
tyre pressure (medium load): front 25 psi, 1.8 atm, rear 25 psi, 1.8 atm.
fuel tank capacity: 8.8 imp gal, 10.6 US gal, 40 1.
carrying capacity: 882 1b, 400 kg© Motor car History
Manuals
-
Ford (europe) Previous 67 / 128 Next
