Horch 830 930 Car Range
830B/830Bk/830BL/951/951A,930V
| Horch 830 car History | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| 830/930 | |
| Production period: | 1933 to 1940 |
| Body versions : | Touring Cars , Roadster ,Sedan , Pullman Limousine , Cabriolet ,Landaulet |
| Engines: | 3.0-3.8 liters (51-67.6 kW) |
| Length: | 4750-5050 mm |
| Width: | 1680-1790 mm |
| Height: | 1600-1650 mm |
| Wheelbase: | 3100-3350 mm |
| Curb weight : | 1650-2100 kg |
The Horch 830 is a car of the luxury class with eight-cylinder - V-engine and rear-wheel drive , which the for Auto Union owned brand Horch at the 23rd International Automobile and Motorcycle Exhibition (IAMA) in February 1933, Berlin (as the successor of type 430 Horch 8 ). The first vehicles came in the fall of 1933 for delivery.
Until the wartime suspension in spring 1940, a total of 11,625 civilian cars Horch 830/930 were built in the Zwickau Horch factory . In addition, received 1934-1937 Reichswehr or army 4,536 Kübelwagen Horch R 830 , which for use in the field - front and rear - in deviation from the civilian types of rigid axles had.
History
Based on the page-controlled twelve-cylinder V-engine of the listening 670/600 over rocker arm actuated horizontally ( "horizontal") valves, Horch-Chief Engineer began Fritz Fiedler with the development of an eight-cylinder V-engine. After Fiedler's move to BMW ( Eisenach branch ) in the summer of 1932, Werner K. Strobel brought the new V8 engine to production maturity. Compared to the previously used eight-cylinder inline engineswith king shaft ( OHC valve control ) and ten crankshaft bearings was the V8 with its triple-mounted crankshaftcheaper to manufacture and also had a shorter length.
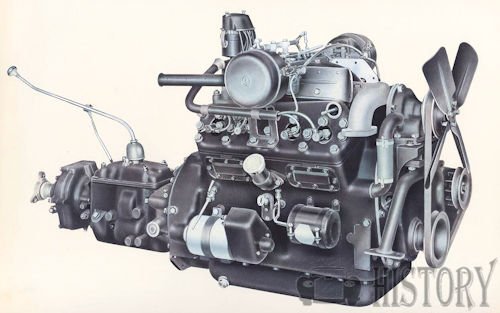
Horch 3-8 litre engine
Like the Horch V12, the V8 engine has a bank angle of 66 degrees. The centrally between the two cylinder banks arranged camshaft is via a triple roller chain driven. However, the "lying" valves do not have the elaborate hydraulic tappet of the twelve-cylinder. A technical feature of the Horch V engines was the kinked interface between the cylinder bank and head , which required specially shaped head gaskets . Through the guidance of intake and exhaust manifoldson the top of the engine this had only a small width. The first version with 3 liters of capacity had 70 hp and thus five more than the 3-liter in-line eight-cylinder of the previous model Horch 430. For the mixture formation made a double - downdraft carburettor from Solex .
The last two versions with 3.5 or 3.8 liters displacement and two Solex flat- gas carburetors were also in the middle ( Horch / Wanderer 901 ) and heavy (Horch 108 on "Einheitsfahrgestell II") unit car of the Wehrmacht - all with Front engine and all-wheel drive - as well as the armored scout Sd.Kfz. 221 and Sd.Kfz. 222 (Horch 801 "unit chassis I" with rear engine and four-wheel drive) used.
The Horch 830 was the second German production car with V8 engine. The National Automobile Society (NAG) presented at the 22nd International Motor Show in February 1931 in Berlin, the NAG V8 (Type 218/219) with 4.5-liter engines. In times of the world economic crisis, however , the 100 hp vehicles were not a success - until 1934, only 50 cars were built.

1936 Horch 830B
Through a four-speed gearbox ( ZF - "Aphon" with helical gears, second to fourth gear were synchronized ), the rear wheels were driven . The shift lever was mounted on the center tunnel. The chassis with rigid axles front and rear corresponded largely to the previous model Horch 430, but the ladder frame was no longer made of open U-profiles, but stiffer box profiles. The Horch 830 had 4 cm more wheelbase (3.2 meters), but weighed only 1650 kg and was thus 200 kg lighter than the Horch 430. Of this accounted for 80 kg on the compact new V8 engine and the rest on the body. The drum brakeswere still mechanically operated via cables. Each a 4-door sedan and a 2-door convertible were offered in classic form and in a more modern design with Stromlinienheck . Their front axles were supported on Halbelliptikfedern; the rear axles had underslung half- springs. With the same chassis of 3.2 meters wheelbase, the 6-seater touring car and the Pullman limousine was offered, the front already a modern double wishbone - independent(upper arm with lower transverse leaf spring) possessed.

Later 1939 Horch 830BL Pullman Limousine
Model changes
Already 1934 appeared the improved Horch 830 B with larger 3.25-Liter-Motor with unchanged 70 HP achievement, hydraulically operated drum brakes ("oil pressure brake") and the front independent suspension on double wishbones also in the four-door sedan and the two-door convertible. The versions with Stromlinienheck accounted for.
The following year, the engine was again increased to 3.5 liters displacement and the now 75 hp model called Horch 830 Bk (k = short) to distinguish with the equally available Horch 830 BL (L = long) with 15 cm more wheelbase (3.35 m) and a rear "double joint axis " ( De-Dion axis ) instead of the rigid axle. This chassis was used for the Pullman sedan, the Pullman Cabriolet and the 4-door Cabriolet.
The 3.5-liter engine was brought in 1937 with two flat- flow carburettors and the increased compression ratio of 6.3: 1 (previously 6.0: 1) to a power of 82 hp. The Horch 930 V (V = shortened) with 10 cm less wheelbase (3.1 m) and a rear double-jointed axle replaced the Horch 830 Bk. In addition to sedan and convertible, there was also a four-door Roadster Cabriolet ( Phaeton ). The long (3.35 m) wheelbase models continued to be called the 830 BL and were available as Pullman saloons, four-door (Pullman) convertibles and six-seater touring cars.
Both Horch V8 models 830 BL and 930 V 1938 received a larger 3.8-liter engine with 92 hp, a "fully synchronized" ZF four-speed gearbox (also 1st gear) and standard a highway - "distance" ( Overdrive ), which was activated with an additional lever.
In 1940, the model 930 L should replace the 830 BL, a 930 S 930 S " Stromlinienfahrzeug " . But this did not happen again after the outbreak of the Second World War . In 1948, four specimens of the Horch 930S were built in small series in Zwickau - but it did not come to a larger series production.
As " Bruhn-Horch " or as the "first and last Horch from Ingolstadt " an automobile was known in 1953 as a unique piece for Richard Bruhn , the first CEO of the Ingolstadt Auto Union GmbH , by hand on the chassis of a Pullman sedan from Type 830 BL was built. His appearance matched the taste of the 1950s, a gently indicated pontoon shape with flowing lines. Few body parts were still made in traditional mixed construction, in which wood was wrapped with steel.
The 2.1 t vehicle has a separating disc between the chauffeur and the passenger compartment as well as reading lights in the rear. With the 92-hp V8 engine, it reached a cruising speed of 120 km / h and a top speed of 125 km / h. Consumption was 19-20 liters per 100 km. The tank was 75 liters.
Technical
-
Technical data of types 830 (until 1936)
Type 830 830 B 830 BL (1935/36) 830 Bk Construction period 1933-1934 1935 1935-1936 1936 constructions T6, PL4, L4, L4S, Cb2, Cb2S L4, Cb2 PL4, PC4, Cb4 L4, Cb2 engine 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock valves standing (sv) standing (sv) standing (sv) standing (sv) Bore × stroke 75 mm × 85 mm 78 mm × 85 mm 78 mm × 92 mm 78 mm × 92 mm capacity 3004 cc 3250 cc 3517 cc 3517 cc Horsepower) 70 70 75 75 Power kW) 51 51 55 55 consumption 17 - 18 l / 100 km 17 l / 100 km 18 l / 100 km 17 l / 100 km top speed 110 - 115 km / h 115 km / h 115 km / h 120 km / h tare 1650 - 1730 kg 1650 kg 1950 kg 1840 kg Perm. total weight 2200 - 2280 kg 2200 kg 2500 kg 2390 kg Electrical 12 volts 12 volts 12 volts 12 volts length 4750 mm 4750 mm 5050 mm 4750 mm width 1780 mm 1780 mm 1780 mm 1680 mm height 1600 - 1650 mm 1600 mm 1650 mm 1600 mm wheelbase 3200 mm 3200 mm 3350 mm 3200 mm Track front / rear 1440 mm / 1470 mm 1440 mm / 1470 mm 1440 mm / 1500 mm 1440 mm / 1470 mm turning circle 12 m 12 m 13.5 m 12 m Technical data types 830 BL and 930 V (1937-1940)
Type 930 V (1937/38) 830 BL (1937/38) 930 V (1938-40) 830 BL (1938-40) Construction period 1937-1938 1937-1938 1938 - 1940 1938 - 1940 constructions L4, Cb2, R2 T6, PL4, PC4, Cb4 L4, Cb2, R2 T6, PL4, PC4, Cb4 engine 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock 8 cyl. V 4 clock valves standing (sv) standing (sv) standing (sv) standing (sv) Bore × stroke 78 mm × 92 mm 78 mm × 92 mm 78 mm × 100 mm 78 mm × 100 mm capacity 3517 cc 3517 cc 3823 cc 3823 cc Horsepower) 82 82 92 92 Power kW) 60.3 60.3 67.6 67.6 consumption 19 l / 100 km 20 l / 100 km 19 l / 100 km 20 l / 100 km top speed 125 km / h 120 km / h 130 km / h 125 km / h tare 1900 kg 2030 kg 1960 kg 2100 kg Perm. total weight 2350 kg 2530 kg 2410 kg 2600 kg Electrical 12 volts 12 volts 12 volts 12 volts length 4920 mm 5050 mm 4920 mm 5050 mm width 1790 mm 1780 mm 1790 mm 1780 mm height 1625 mm 1650 mm 1625 mm 1650 mm wheelbase 3100 mm 3350 mm 3100 mm 3350 mm Track front / rear 1440 mm / 1470 mm 1440 mm / 1500 mm 1440 mm / 1470 mm 1440 mm / 1500 mm turning circle 11.5 m 13.5 m 11.5 m 13.5 m
