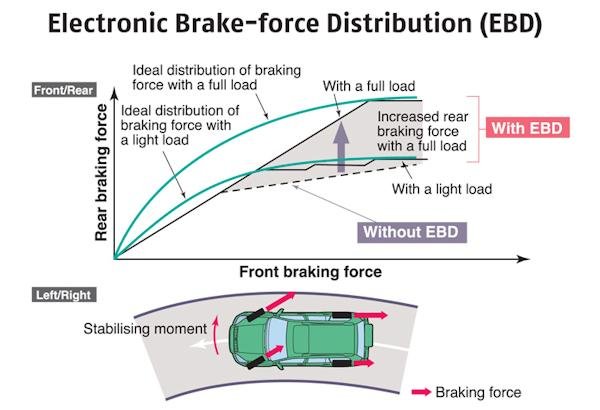
Electronic brakeforce distribution (EBD)
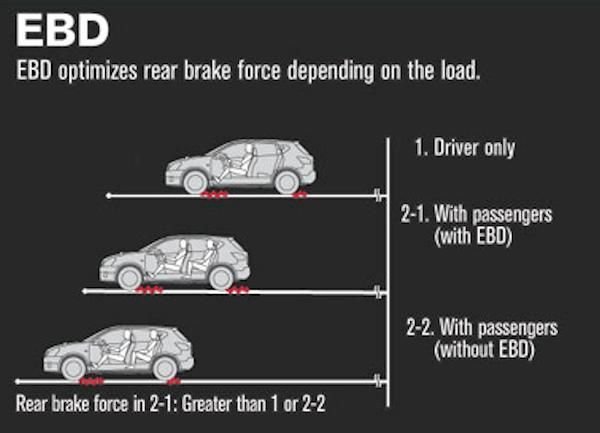
Electronic brakeforce distribution (EBD or EBFD), Electronic brakeforce limitation (EBL) is an automobile brake technology that automatically varies the amount of force applied to each of a vehicle's brakes, based on road conditions, speed, loading, etc. Always coupled with anti-lock braking systems, EBD can apply more or less braking pressure to each wheel in order to maximize stopping power whilst maintaining vehicular control Typically, the front end carries the most weight and EBD distributes less braking pressure to the rear brakes so the rear brakes do not lock up and cause a skid. In some systems, EBD distributes more braking pressure at the rear brakes during initial brake application before the effects of weight transfer become apparent.
How EBD works
As per SAE - Buschmann et al. "The job of the EBD as a subsystem of the ABS system is to control the effective adhesion utilization by the rear wheels. The pressure of the rear wheels is approximated to the ideal brake force distribution in a partial braking operation. To do so, the conventional brake design is modified in the direction of rear axle overbraking, and the components of the ABS are used. EBD reduces the strain on the hydraulic brake force proportioning valve in the vehicle. EBD optimizes the brake design with regard to: adhesion utilization; driving stability; wear; temperature stress; and pedal force."
EBD may work in conjunction with ABS and Electronic Stability Control ("ESC") to minimize yaw accelerations during turns. ESC compares the steering wheel angle to vehicle turning rate using a yaw rate sensor. "Yaw" is the vehicle's rotation around its vertical center of gravity (turning left or right). If the yaw sensor detects more/less yaw than the steering wheel angle should create, the car is understeering or oversteering and ESC activates one of the front or rear brakes to rotate the car back onto its intended course. For example, if a car is making a left turn and begins to understeer (the car plows forward to the outside of the turn) ESC activates the left rear brake, which will help turn the car left. The sensors are so sensitive, and the actuation is so quick that the system may correct direction before the driver reacts. ABS helps prevent wheel lock-up and EBD helps apply appropriate brake force to make ESC work effectively and easily.