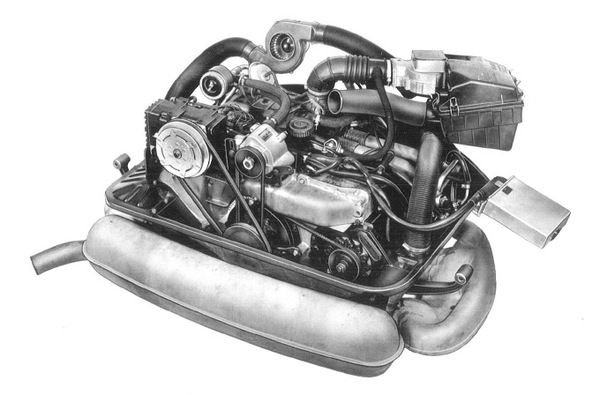
Volkswagen Type 4 engine
 | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1968–1983 |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Volkswagen Type 1 engine |
| Successor | Volkswagen Wasserboxer engine |
In 1968, Volkswagen introduced a new vehicle, the Volkswagen Type 4. The model 411, and later the model 412, offered many new features to the Volkswagen lineup.
While the Type 4 was discontinued in 1974 when sales dropped, its engine became the power plant for Volkswagen Type 2s produced from 1972 to 1979: it continued in modified form in the later Vanagon which was air-cooled from 1980 until mid-1983.
The engine that superseded the Type 4 engine in late 1983 retained Volkswagen Type 1 architecture, yet featured water-cooled cylinder heads and cylinder jackets. The wasserboxer, Volkswagen terminology for a water-cooled, opposed-cylinder (flat or 'boxer engine') was subsequently discontinued in 1992 with the introduction of the Eurovan.
The Type 4 engine was also used on the Volkswagen version of the Porsche 914. Volkswagen versions originally came with an 80 horsepower (60 kW) fuel-injected 1.7-litre flat-4 engine based on the Volkswagen air-cooled engine. In Europe, the four-cylinder cars were sold as Volkswagen-Porsches, at Volkswagen dealerships.
Porsche discontinued the 914/6 variant in 1972 after production of 3,351 units; its place in the lineup was filled by a variant powered by a new 95 metric horsepower (70 kW; 94 bhp) 2.0-litre fuel-injected version of Volkswagen's Type 4 engine in 1973. For 1974, the 1.7-litre engine was replaced by a 76 metric horsepower (56 kW; 75 bhp) 1.8-litre, and the new Bosch L-Jetronic fuel injection system was added to American units to help with emissions control. 914 production ended in 1976. The 2.0-litre engine continued to be used in the Porsche 912E, which provided an entry-level model until the Porsche 924 was introduced.
For the Volkswagen Type 2, 1972's most prominent change was a bigger engine compartment to fit the larger 1.7- to 2.0-litre engines from the Volkswagen Type 4, and a redesigned rear end which eliminated the removable rear apron. The air inlets were also enlarged to accommodate the increased cooling air needs of the larger engines.
This all-new, larger engine is commonly called the Type 4 engine as opposed to the previous Type 1 engine first introduced in the Type 1 Beetle. This engine was called "Type 4" because it was originally designed for the Type 4 (411 and 412) automobiles. There is no "Type 2 engine" or "Type 3 engine", because those vehicles did not feature new engine designs when introduced. They used the "Type 1" engine from the Beetle with minor modifications such as rear mount provisions and different cooling shroud arrangements, although the Type 3 did introduce fuel injection on the "Type 1" engine.
In the Type 2, the Volkswagen Type 4 engine was an option from 1972. This engine was standard in models destined for the US and Canada. Only with the Type 4 engine did an automatic transmission become available for the first time in 1973. Both engines displaced 1.7 litres, rated at 66 metric horsepower (49 kW; 65 bhp) with the manual transmission, and 62 metric horsepower (46 kW; 61 bhp) with the automatic. The Type 4 engine was enlarged to 1.8 litres and 68 metric horsepower (50 kW; 67 bhp) in 1974, and again to 2.0 litres and 70 metric horsepower (51 kW; 69 bhp) in 1976. As with all Transporter engines, the focus in development was not on motive power, but on low-end torque. The Type 4 engines were considerably more robust and durable than the Type 1 engines, particularly in Transporter service.
| Volkswagen 1700 engine | |
|---|---|
| Combustion chamber | |
| Displacement | 1,679 cc (102.5 cu in) |
| Compression ratio | 7.8:1 |
| Output | |
| Power output | 76 PS (56 kW) @ 5,000 rpm |
| Torque output | 127 N·m (94 lbf·ft) @ 3,500 rpm |
| Volkswagen 1800 engine | |
|---|---|
| Power output | 50 kW (68 PS; 67 bhp) |
| Volkswagen 2000 engine | |
|---|---|
| Power output | 52 kW (71 PS; 70 bhp) |
Uprated Volkswagen Type-4 engine with twin carbs

Description
Technical
-
Technical details and specifications VW Type 4 engine (1968-1983)
Volkswagen Transporter 1.7 L Type 4 engine
No. of cylinders 4
Capacity 1679 cc
Firing order 1-4-3-2
Compression ratio 7.3:1
Suitable for unleaded petrol No
Fuel system Make Solex 34 PDSIT Carb-FJ
Ignition coil Make Bosch 0 221 102 076
Distributor Make Bosch 021 905 205E
Distributor Contact breaker gap 0.4mm
Starter motor Make Bosch Type EF(L)12V 0.7PS
Minimum starting voltage 9V
Maximum cranking amps 119-145a
Alternator Make Bosch AD1/14V
Regulated voltage 13.9-14.8V© Motor car History
-
Service Guide VW Type 4 engine (1968-1983)
Volkswagen Transporter 1.7 L Type 4 engine
Spark plugs Electrode gap 0.7mm
Spark plugs Tighten 36 Nm
Spark plugs Original equipment Bosch W8CC
Spark plugs Make Champion N5C
Spark plugs Make NGK B5ES
Valve clearance -INLET 0.15 mm check cold
Valve clearance -EXHAUST 0.15 mm check cold
Drive belt size - alternator 9.5x965mm
Drive belt tension - alternator 15 mm
Engine oil grade - moderate climate 10W/30 SAE
Engine oil change 3 litres
Manual gearbox oil change 2 litres
Automatic transmission oil change 3 litres© Motor car History


