Car Self aligning torque explained
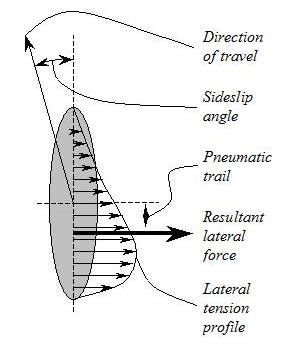
Self aligning torque, also known as aligning torque, SAT, or Mz, is the torque that a tire creates as it rolls along, which tends to steer it, i.e. rotate it around its vertical axis. In the presence of a non-zero slip angle, this torque tends to steer the tire toward the direction in which it is traveling, hence its name.
The magnitude of this torque can be calculated as the product of the lateral force generated at the contact patch and the distance behind the wheel centre at which that force acts. This distance is known as the pneumatic trail. The steering torque around a non-vertical steer axis with non-zero mechanical trail is given by (trail+pneumatic trail)*cos(caster angle)*Fy.
Even if the slip angle and camber angle are zero, and the road is flat, this torque will still be generated due to asymmetries in the tire's construction and the asymmetrical shape and pressure distribution of the contact patch. Typically for a production tire this torque reaches a maximum at 2-4 degrees of slip (this figure is very dependent on a lot of things) and falls to zero as the tire reaches its maximum lateral force capability.

